My interest in using the command prompt(cmd) continues to grow,primarily because of how much time it saves me. However, using it daily means typing repititive commands which becomes tedious. Accessing frequently used directories means repeatedly typing cd (command for change directory) along with directory paths. This is where batch programming comes in.
Note: directory and folder refer to the same thing
Batch programming, also known as batch scripting, involves using batch files(or batch scripts) to execute commands. A batch file contains a set of commands that are executed in a computer,mostly system tasks. I use batch scripts to streamline repetitive actions. For instance, you can create a batch script to launch your favourite apps when your computer starts. In this article, I demonstrate how to use a batch script to quickly switch my current working directory to a desired location using a shortcut, avoiding the need to repeatedly type cd commands and paths.
Getting started
Open your home directory which is usually C:\Users\user, where the name user is replaced by your system username.
 Alternatively, starting the cmd will set you in this directory.
Alternatively, starting the cmd will set you in this directory.
Create a folder called .cmds. The filepath will look like this:
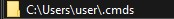
Open .cmds and create a text file . Save it as cmds.bat. This file will store your commands, which will be written as plain text — highlighting the power and simplicity of batch scripting.
Right-click cmds.bat and select Edit.
Suppose I want to open a directory containing my books in the cmd session I’m in. The structure of the command will be doskey shortcut_name = <command> "<filepath>". Copy this into your file :
@echo off
doskey b=cd "C:\Users\user\Desktop\ALLDocs\books"
Explanation:@echo off stops the cmd from displaying commands as they execute.
doskey initializes the shortcut.
b is the shortcut name. This is what you will type in the cmd and you can change it to whatever suits you.
cd means change directory, which is the command for changing directory. It directs the cmd to change the current working directory to "C:\Users\user\Desktop\ALLDocs\books". Replace this with any path you frequently use.
Save the file after editing. You can add more commands to this file later.
One last step, you need to modify the Windows Registry for you to use the commands available in cmds.bat.
Click Start and type regedit. This will guide you to Registry Editor.
Access Command Processor folder by following this path: HKEY_CURRENT_USER > Software > Microsoft > Command Processor
Right-Click to get such a pop-up:
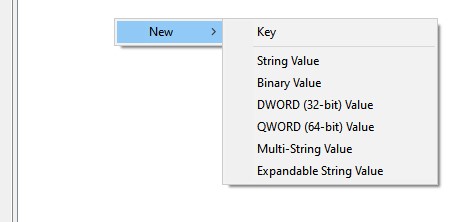
Select String Value and name it AutoRun. For the Value column, enter the full path to the cmds.bat file you created earlier - e.g. C:\Users\user\.cmds\cmds.bat
Once you are done setting this, the list in Command Processor should have this:

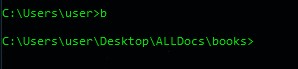
Let’s confirm if the shortcut is working. Open a new cmd session (don’t use any cmd session that was open before editing the Registry).
Run the shortcut. My current working directory moves to the target directory books.
Thank you for reading my first blog.